关于病毒的解剖学、结构及疾病。
Anatomy and Structure of Viruses
By Regina Bailey
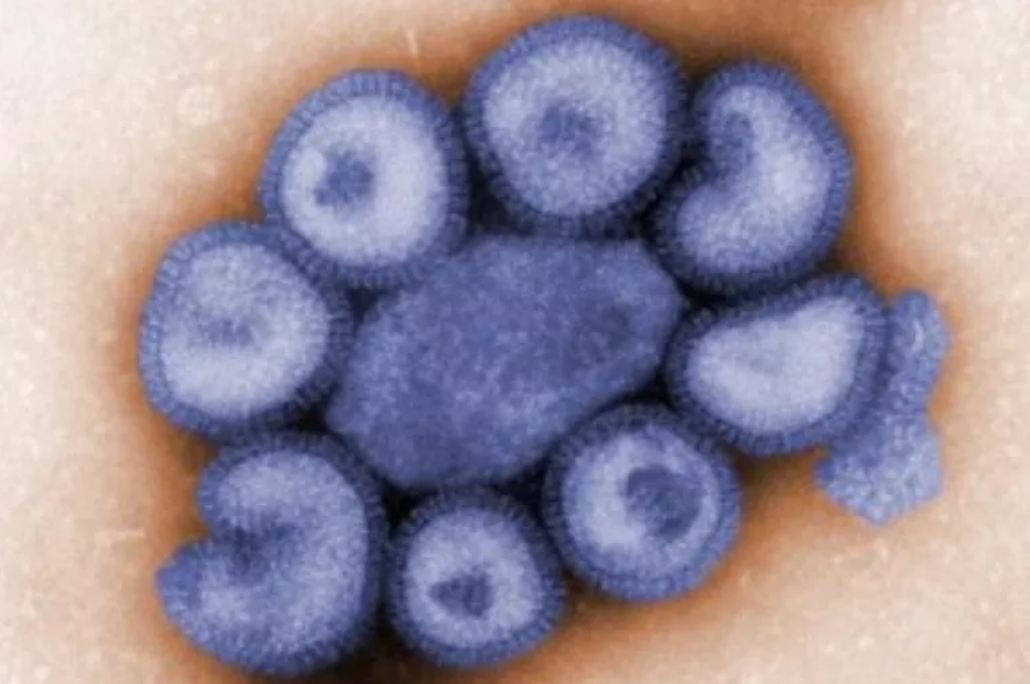 CDC / Dr. F. A. Murphy
CDC / Dr. F. A. Murphy
Scientists have long sought to uncover the structure and function of viruses. Viruses are unique in that they have been classified as both living and nonliving at various points in the history of biology. Viruses are not cells but non-living, infectious particles. They are capable of causing a number of diseases, including cancer, in various different types of organisms.
Viral pathogens not only infect humans and animals, but also plants, bacteria, protists, and archaeans. These extremely tiny particles are about 1,000 times smaller than bacteria and can be found in almost any environment. Viruses can not exist independently of other organisms as they must take over a living cell in order to reproduce.
Virus Anatomy and Structure
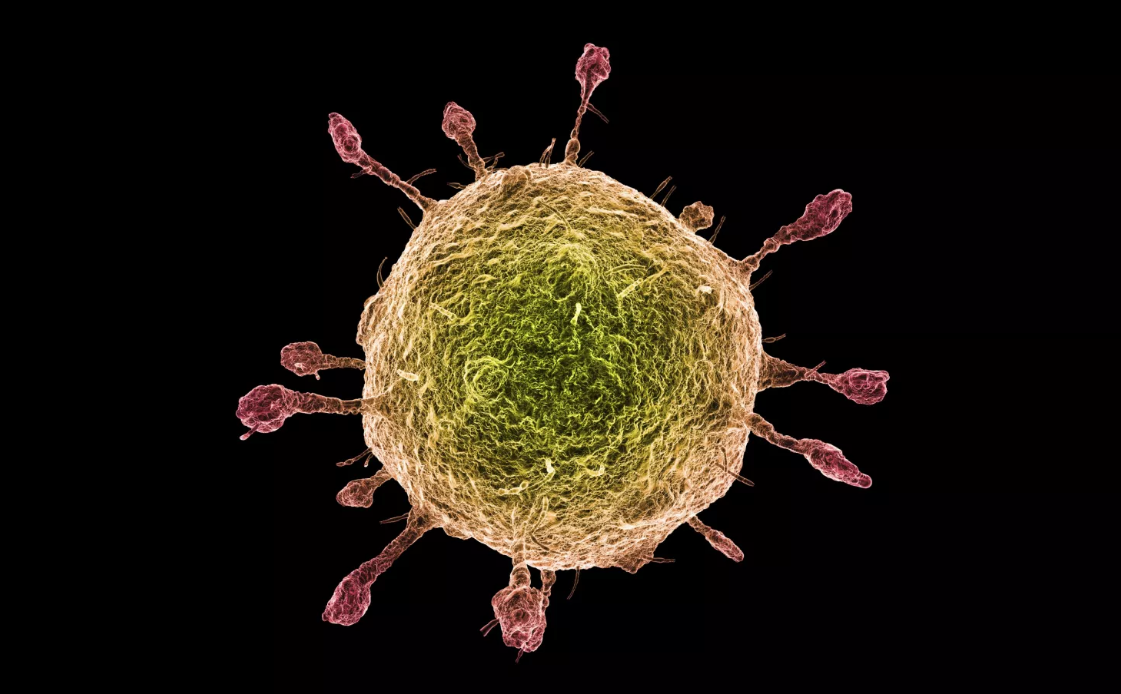 Alfred Pasieka/Science Photo Library/Getty Images
Alfred Pasieka/Science Photo Library/Getty Images
A virus particle, also known as a virion, is essentially nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) enclosed within a protein shell or coat. Viruses are extremely small, approximately 20 - 400 nanometers in diameter. The largest virus, known as the Mimivirus, can measure up to 500 nanometers in diameter. By comparison, a human red blood cell is around 6,000 to 8,000 nanometers in diameter.
In addition to varying sizes, viruses also have a variety of shapes. Similar to bacteria, some viruses have spherical or rod shapes. Other viruses are icosahedral (polyhedron with 20 faces) or helical shaped. Viral shape is determined by the protein coat that encases and protects the viral genome.
Viral Genetic Material
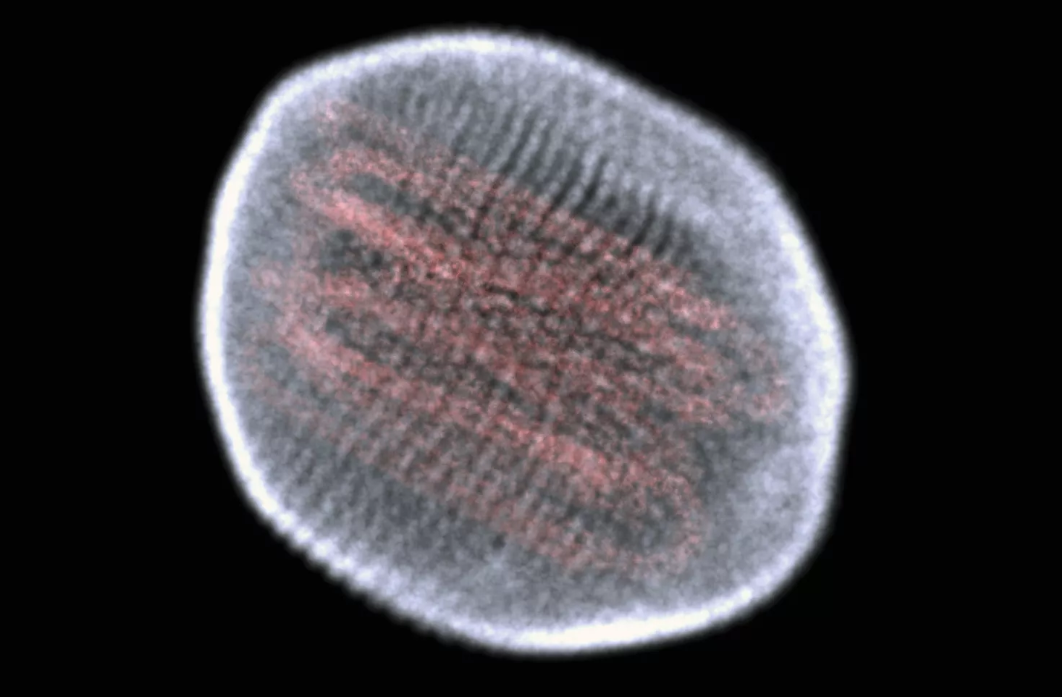 Equinox Graphics/Science Photo Library/Getty Images
Equinox Graphics/Science Photo Library/Getty Images
Viruses may have double-stranded DNA, double-stranded RNA, single-stranded DNA or single-stranded RNA. The type of genetic material found in a particular virus depends on the nature and function of the specific virus. The genetic material is not typically exposed but covered by a protein coat known as a capsid. The viral genome can consist of a very small number of genes or up to hundreds of genes depending on the type of virus. Note that the genome is typically organized as a long molecule that is usually straight or circular.
Viral Capsid
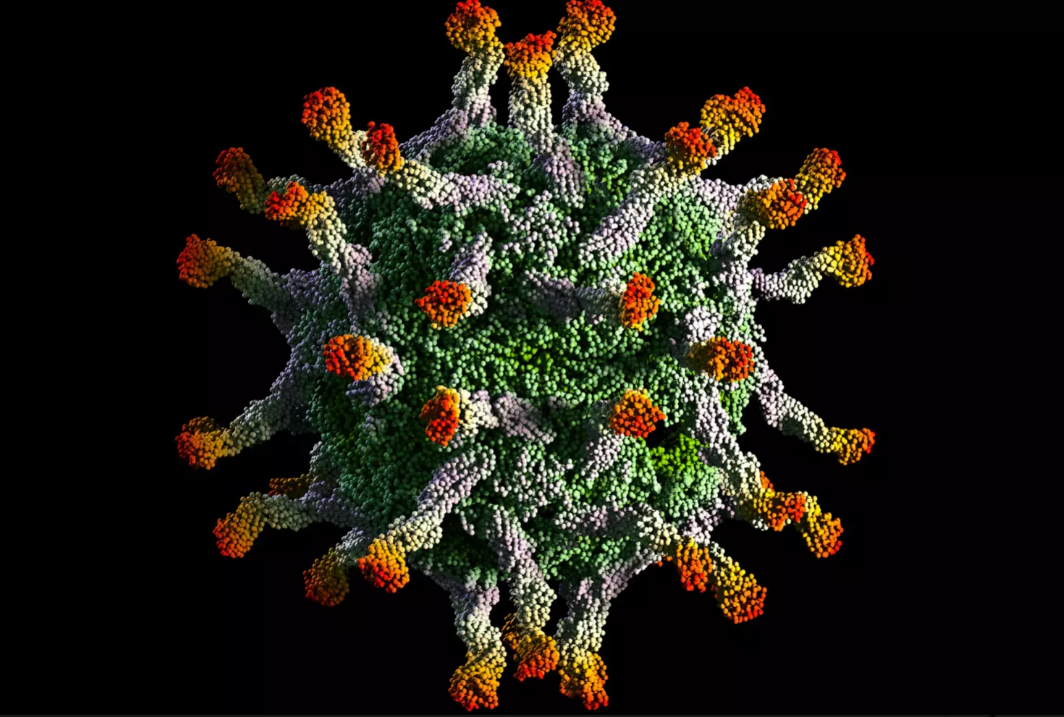 Theasis/E+/Getty Images
Theasis/E+/Getty Images
The protein coat that encases viral genetic material is known as a capsid. A capsid is composed of protein subunits called capsomeres. Capsids can have several shapes: polyhedral, rod or complex. Capsids function to protect the viral genetic material from damage.
In addition to the protein coat, some viruses have specialized structures. For example, the flu virus has a membrane-like envelope around its capsid. These viruses are known as enveloped viruses. The envelope has both host cell and viral components and assists the virus in infecting its host. Capsid additions are also found in bacteriophages. For example, bacteriophages can have a protein "tail" attached to the capsid that is used to infect host bacteria.
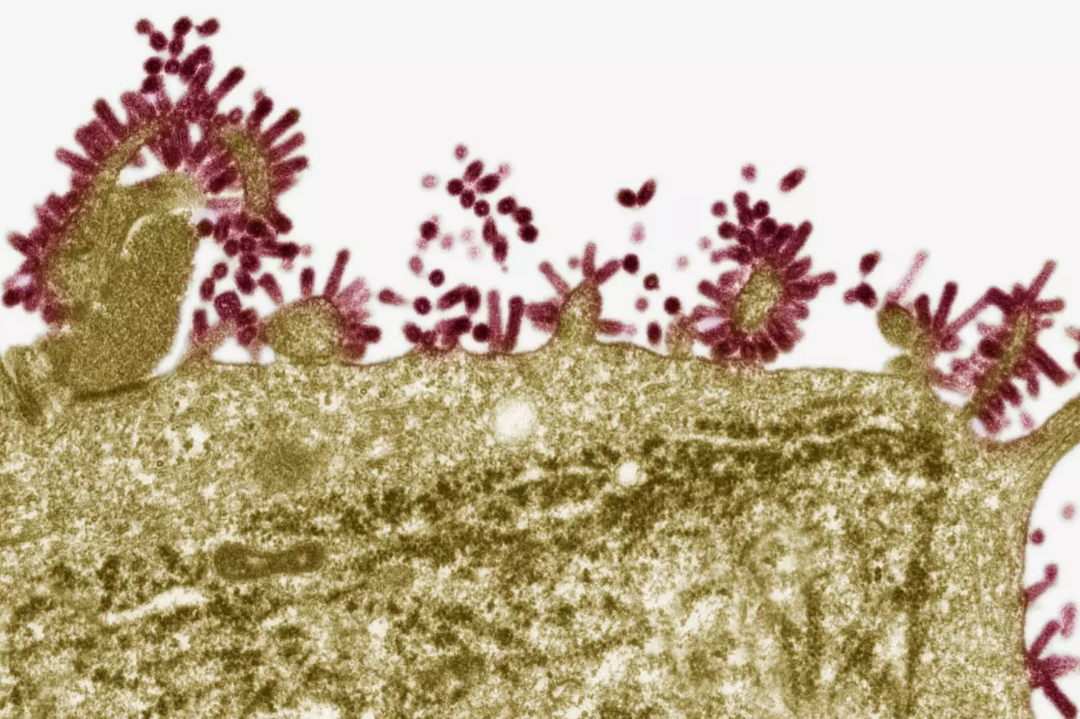
Virus Replication
 Steve Gschmeissner/Science Photo Library/Getty Images
Steve Gschmeissner/Science Photo Library/Getty Images
Viruses are not capable of replicating their genes by themselves. They must rely on a host cell for reproduction. In order for viral replication to occur, the virus must first infect a host cell. The virus injects its genetic material into the cell and uses the cell's organelles to replicate. Once a sufficient number of viruses have been replicated, the newly formed viruses lyse or break open the host cell and move on to infect other cells. This type of viral replication is known as the lytic cycle.
Some viruses can replicate by the lysogenic cycle. In this process, viral DNA is inserted into the DNA of the host cell. At this point, the viral genome is known as a prophage and enters a dormant state. The prophage genome is replicated along with the bacterial genome when the bacteria divide and is passed along to each bacterial daughter cell. When triggered by changing environmental conditions, the prophage DNA may become lytic and start replicating viral components within the host cell. Viruses that are non-enveloped are released from the cell by lysis or exocytosis. Enveloped viruses are commonly released by budding.
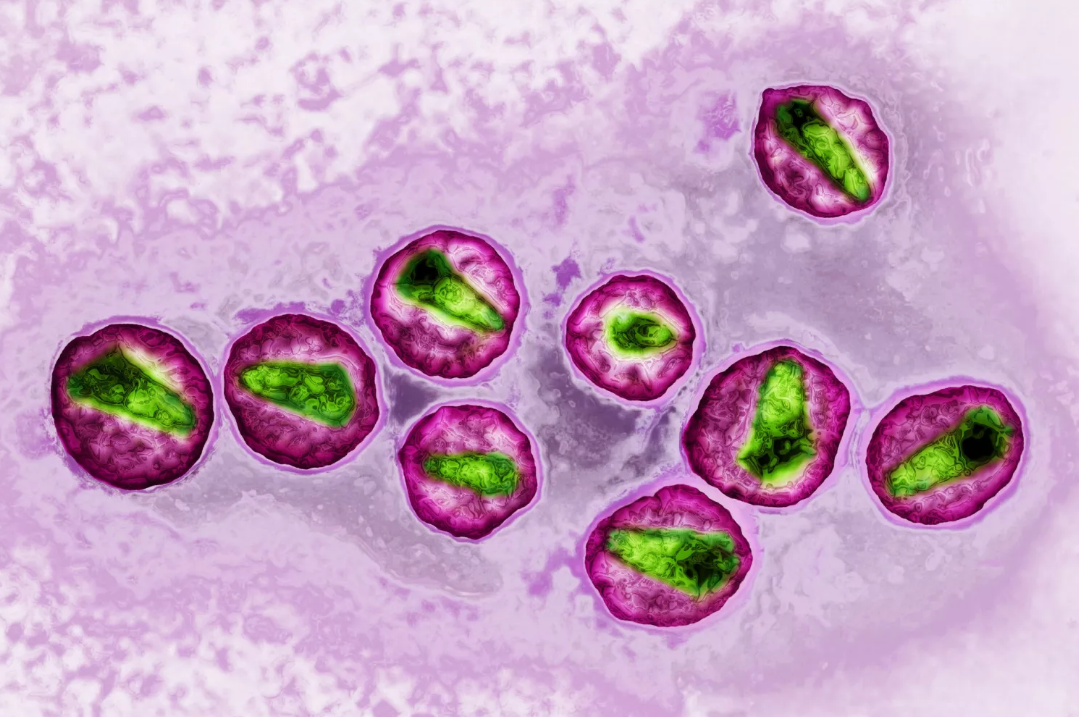
Viral Diseases
 BSIP/UIG/Getty Images
BSIP/UIG/Getty Images
Viruses cause a number of diseases in the organisms they infect. Human infections and diseases caused by viruses include Ebola fever, chicken pox, measles, influenza, HIV/AIDS, and herpes. Vaccines have been effective at preventing some types of viral infections, such as small pox, in humans. They work by helping the body to build an immune system response against specific viruses.
Viral diseases that impact animals include rabies, foot-and-mouth disease, bird flu, and swine flu. Plant diseases include mosaic disease, ring spot, leaf curl, and leaf roll diseases. Viruses known as bacteriophages cause disease in bacteria and archaeans.